Paediatric Hearing Tests
Full hearing assessments for children ages 5+
Consultation Charge €150.

The assessment process
The Audiologists will explain the purpose of the appointment, including the referral source and give a brief overview of the assessment process. The assessment process includes the following steps:
- A full case history will be obtained by the Audiologists.
- Otoscopy will be performed safely as per the BSA Recommended Procedure.
- Play Audiometry/Pure-tone Audiometry will be performed safely as per the BSA Recommended Procedure.
- Tympanometry will be performed safely as per the BSA Recommended Procedure.
- Transient Evoked Otoacoustic Emissions will be performed as per the HSE NHSP Guidelines for New-born Early Audiological Assessment.
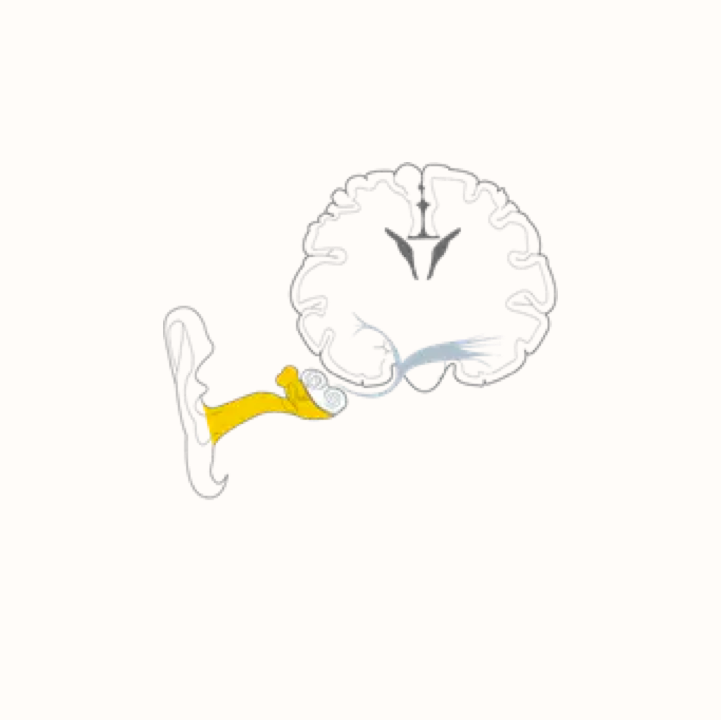
Conductive hearing loss
The most common type of hearing loss in the paediatric population. It typically occurs due to a problem transmitting sounds at the level of the external or middle ear. The major cause of conductive hearing loss in children is otitis media with effusion (glue ear)
Otitis media with effusion (OME) is a collection of non-infected fluid in the middle ear space. This fluid may accumulate in the middle ear as a result of a cold, sore throat or upper respiratory infection.
OME is usually self-limited, which means, the fluid usually resolves on its own within 4 to 6 weeks. However, in some instances the fluid may persist for a longer period of time and cause a temporary decrease in hearing or the fluid may become infected (acute otitis media).
While signs of OME can vary from child to child and change in intensity, common symptoms include:
- Hearing difficulties
- Tugging or pulling at one or both ears
- Loss of balance
- Delayed speech development
The Audiologists will identify, monitor and refer onwards to an ENT consultant (if necessary).
Sensorineural hearing loss
Permanent hearing loss which results from a disruption of the auditory pathway at any point from the cochlea of the inner ear through to the brainstem. The most common causes of SNHL include- Genetic factors, meningitis, ototoxic medication.
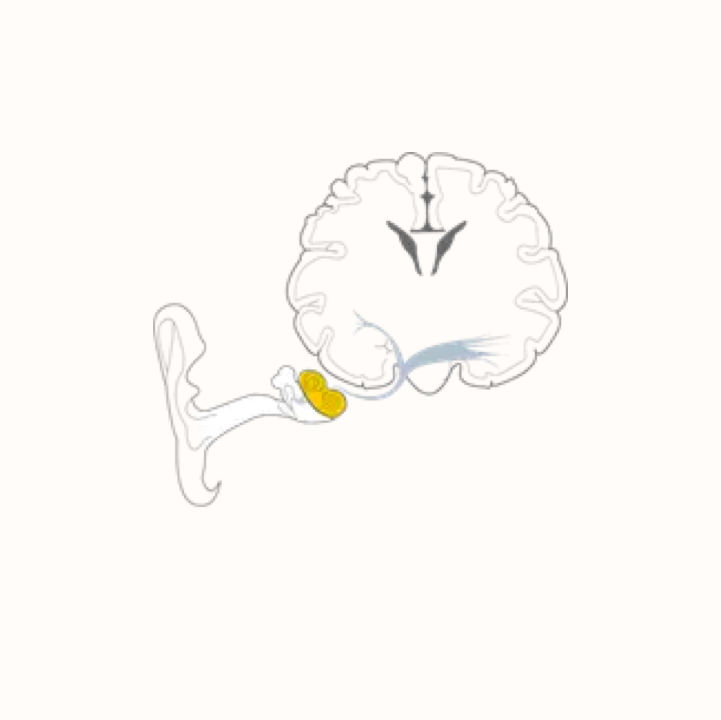
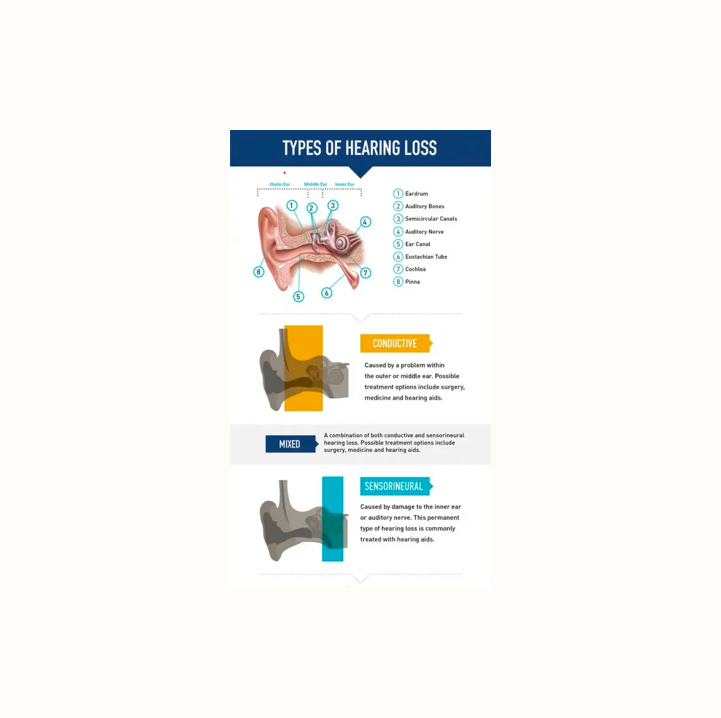
Mixed hearing loss
Mixed hearing loss occurs when there are both conductive and sensorineural components.
Some indicators of hearing loss can include:
- Concerns with speech and language development.
- Not responding when called.
- Difficulty identifying which direction a sound comes from.
- Family history of hearing difficulties.
- Pulling / tugging at ears.
- Loss of Balance.
- Inattentiveness.
- Wanting the television or radio louder than usual.
- Misunderstanding directions.
Start your path to better hearing

